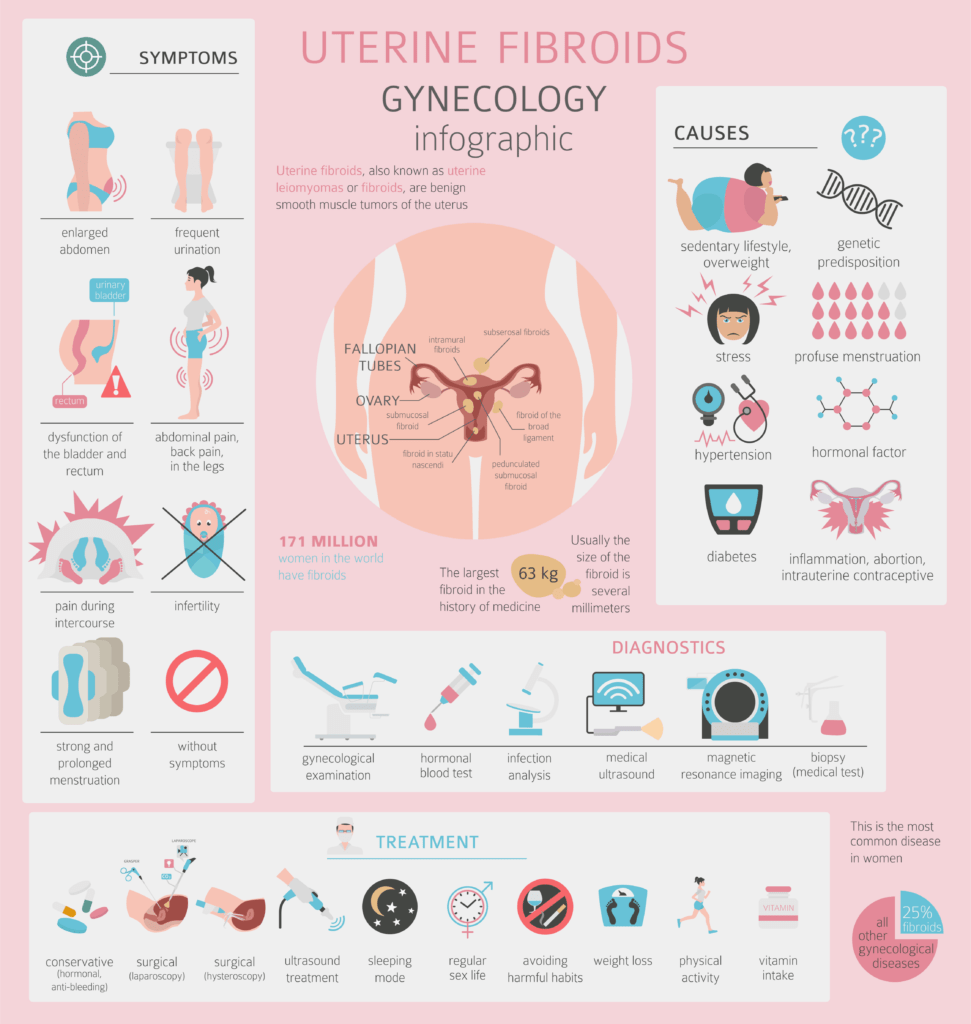
Fibroids are abnormal muscular growths that grow in or on a woman’s uterus. They are usually non-cancerous (benign) and very rarely turn into cancer. They are also called leiomyomas or myomas.
They can grow in the womb, within and on the uterine wall. It can just eb one in the uterus or there can be multiple in one uterus. They can be as small as a seed or very large that they affect the shape and size of the womb. They come In different sizes and some can attach to the womb on a stalk.
They are most common in women of child-bearing age (30-40 yrs old, though they can show up at any age) and almost always shrink after menopause. They are also more common in African-American women than white women, most likely due to genetic disposition and diet.
A lot of women who have fibroids don’t know they have them and are discovered by chance during a routine pelvic exam/ultrasound.
Risk factors for developing fibroids.
- Age. Fibroids become more common as women approach childbearing age, usually between ages 30-40.
- Family history. If a mother or aunty has had fibroids, the risk of having them is about three times higher than average.
- Ethnicity African-American women are more likely to develop fibroids than other racial groups.
- Obesity. Women who are overweight are at higher risk for fibroids.
- Eating a lot of red meat (e.g. beef) and ham is linked with a higher risk of fibroids. Eating plenty of green vegetables seems to protect women from developing fibroids.
- Starting your period early
- Vitamin D deficiency.
Types of uterine fibroids
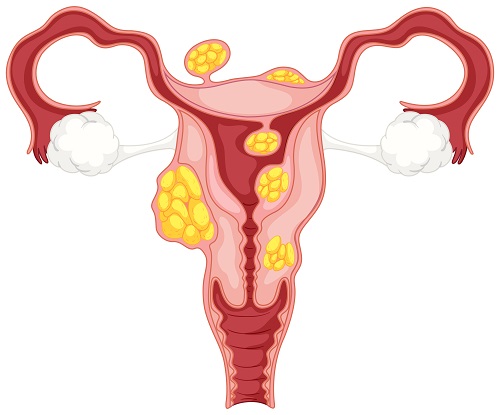
Fibroids are named/classed based on where they grow:
- Intramural fibroids: These grow within the muscular wall of the uterus and are the most common types of fibroids.
- Submucosal fibroids: They grow beneath womb’s lining and into the uterine cavity.
- Subserosal fibroids: fibroids grow on the outside of the uterus into the pelvis and can become very big, making the tummy look distended.
- Pendunculated fibroids: These are fibroids which are located anywhere in the uterus are attached to the womb with a narrow stalk of tissue. They may look like mushrooms.
Causes of fibroids
No one knows for sure what causes fibroids. Researchers think that more than one factor could play a role though they are majorly influenced by hormones. These factors could be:
- Hormones especially oestrogen: This is because fibroids usually develop when oestrogen levels are at its peak during a woman’s reproductive years and shrink when menopause sets in.
- Hereditary (runs in families)
- Pregnancy
Symptoms of fibroids
Most fibroids do not cause any symptoms, but some women with fibroids can have:
- Heavy bleeding or painful periods
- Feeling of fullness in the pelvic area (lower stomach area)
- Frequent urination
- Pain during sex
- Lower back pain
- Complications during pregnancy and labor, which could lead to cesearan.
- Depending on location, it can cause infertility
How are they diagnosed
Some women may not have sympotoms and fibroids are only discovered through a routine pelvic examination.
If fibroids are suspected, your doctor may be able to feel the fibroid by using his/her fingers to feel the size of your uterus and may feel a painless lump.order tests to check for fibroids.
To investigate further, your doctor can order imaging tests or minor surgical procedures which uses sound waves to create an image of the inside of the body.
- Ultrasound – Your doctor can use an abdominal (where the probe is moved over the outside of your tummy) or transvaginal ( where the probe is inserted into your vagina) to view inside your uterus.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – Uses magnets and radio waves to produce the picture
- Hysterosalpinogram or sonohysterogram – A sonohysterogram involves injecting water into the uterus and taking ultrasound pictures while Hysterosalpinogram involves injecting the use of x-ray dye and taking x-ray pictures..
- Laparoscopy – This procedure involves the surgeon making a small incision in your abdomen and passing the laparoscope into your abdomen to view the organs in your abdomen and pelvis. During this procedure, you will normally be given anaesthetic so you should be asleep during the procedure.
Treatment of fibroids
In most cases, fibroids are asymptomatic and don’t cause any problems. As a result, doctors often recommend watchful waiting because they usually shrink after menopause.
However, in case that they are causing problems, there are different methods that can be used on its own or using therapies like surgery, hormonal medications and any other treatment.
Medications
They can be used to shrink or control the symptoms of fibroids.
Progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD) / birth control pills : This can be used to control heavy bleeding as well as act as a form of birth control. It doesn’t make fibroid disappear or shrink. This is the same of progesterone-like injections like Depo-Provera.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists: These stop the production of estrogen and progesterone, thereby stopping the menstrual cycle temporarily. This would then cause fibroids to shrink as their growth are normally fuelled by hormones. Example sof GnRH agonists include Lupron and is nornmally given by injectins, implants or nasal spray. There are side efefcts, which include insomnia. decreased sex drive. Using GnRH agonist is normally limited to 3-6 months as it can cause loss of bone.
Tranexamic acid: This is normally used to ease heavy bleeding during a woman’s period and is only used on heavy bleeding days.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) : are used to treat pain relating to fibroids, but don’t control bleeding or growth of fibroids.
If the fibroids are causing moderate or severe symptoms, then the follwoing may be recommended:
Uterine artery embolization: This is when small gel particles are injected into the blood vessels that supply blood t the fibroid, therefore cutting off blood supply enabling them to shrink. This is very effective when trying to shrink fibroids , but complications may happen if the blood supply to other organs are tampered with. Also, UFE does not work with all types of fibroids
Myolysis/ Cryomyolysis: is when the fibroids are removed using electric curremt/freezing with the aid of a needle ( usually guided by laparoscopy)
Myomectomy: This is a surgical procedure where the fibroids are removed without removing the uterus. This procedure is ideal for women who still want to retain their fertility and get pregnant in future. Myomectomy can be performed in three ways:
- Abdominal : is when the fibroids are removed through an open surgical cut in your abdomen
- Laparoscopic myomectomy: is less invasive than abdominal and the fibroids are removed through several small incisions.
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy: is when the fibroids are removed using a special scope put through the vagina and cervix.
Endometrial ablation: This is when the lining of the uteris is removed and can be done with laser, freezing, microwaves, wire loops. This procedure affects fertility and women cannot get pregnant after thsi procedure.
Natural approach to fibroids.
Several lifestyle factors have also been linked the growth of fibroids in women.
At-home care, diet changes, and natural remedies may help treat fibroids and relieve symptoms. The lifestyle changes below are also important in the prevention of fibroids.
These natural treatments may or may not help your fibroid symptoms, since relief depends on how severe your symptoms are and how your fibroids have progressed. You should speak with your doctor before trying any of these options.
Eating right by avoiding a lot of red beef, white rice and pasta, alcohol, and replacing with lean beef, whole grains, legumes oily fats can help reduce fibroids. Attaining a healthy BMI is important as excess weight has been linked to fuelling estrogen which then stimulates the growth of fibroids.