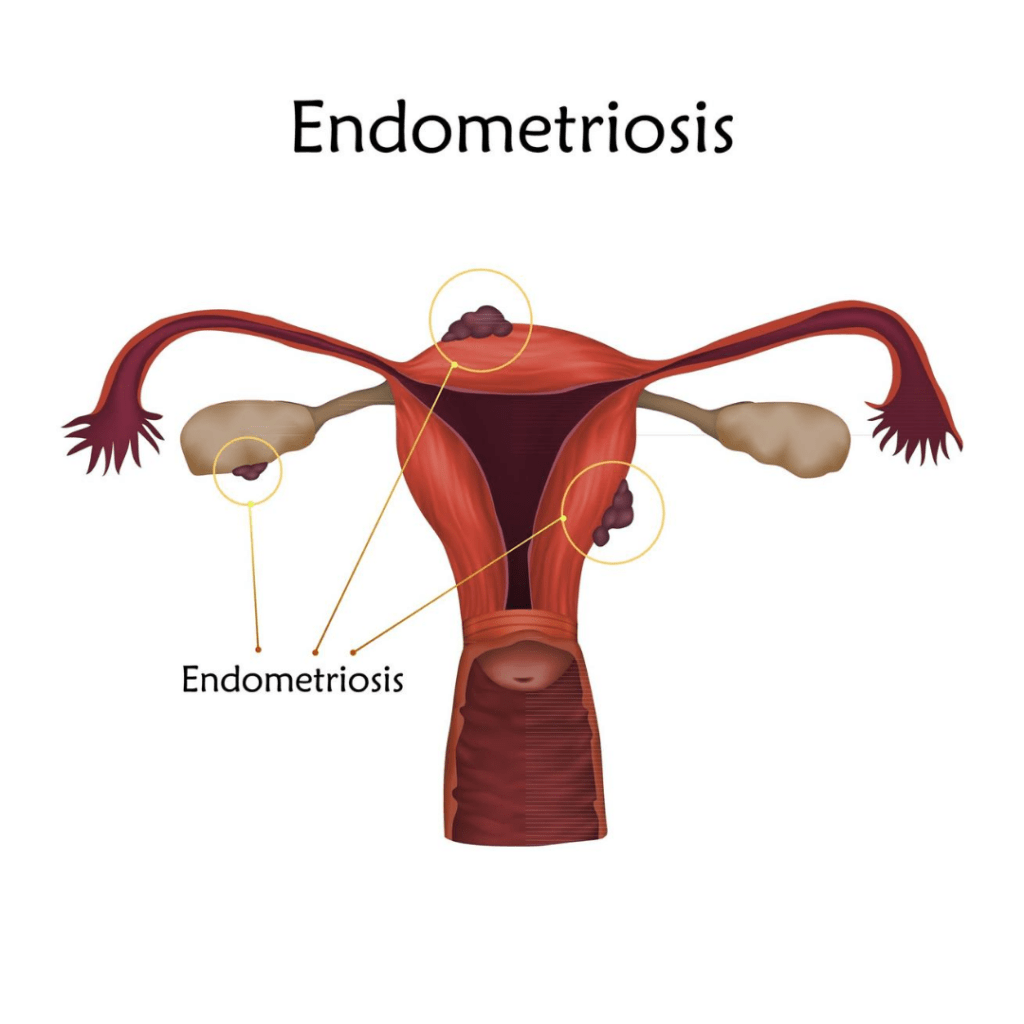
This is when the tissue similar to the lining of the womb (endometrium) starts to grow in other places, such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It can also grow in the vagina, cervix, vulva, bowel, bladder, or rectum.
Rarely, endometriosis appears in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, brain, and skin. Endometriosis can affect women of any age and especially common among women in their 30s and 40s.
It’s a long-term condition that can have a significant impact on your life, but there are treatments that can help.
Symptoms of endometriosis
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary. Some women are badly affected, while others might not have any noticeable symptoms.
The main symptoms of endometriosis are:
- pain – in your lower tummy (pelvis) or back , during your period, very painful menstrual cramps, during/after sex, pain when peeing or pooing during your period, leg pain
- Bleeding/spotting between periods
- Infertility – a significant long-term impact. Some women may realise this is the cause after investigating. Surgery to remove endometriosis tissue can help improve your chances of getting pregnant, although there’s no guarantee that you’ll be able to get pregnant after treatment.
- Digestive orders- Bloating, Diarrhea, constipation
You may also heavy periods. You might use lots of pads or tampons, or you may bleed through your clothes.
For some women, endometriosis can have a big impact on their life and may sometimes lead to feelings of depression.
Causes of endometriosis
The cause of endometriosis is not known.
Several theories have been suggested, including:
- genetics – the condition tends to run in families, and affects people of certain ethnic groups more than others
- when some of the womb lining flows up through the fallopian tubes and implants itself on the organs of the pelvis, rather than leaving the body as a period. This is called retrograde menstrual flow
- a problem with the immune system, the body’s natural defence against illness and infection. Your body may find it difficult to destroy endometrial tissue growing out of place.
- Surgery – During surgery around the pelvic/abdominal area, endometrial tissue could be moved and put pain the abdomen by mistake.
- Hormones – It appears the hormone estrogen appears to promote endometriosis.
Treatments for endometriosis
Experts say there’s currently no cure for endometriosis, but there are treatments that can help ease the symptoms.
Treatments include:
- For mild symptoms, you can use over the counter painkillers – such as NSAIDs and paracetamol.
- Hormone medicines and contraceptives – including the combined pill, the hormonal IUD , and medicines called gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues (if hormones and pain killers are not working )
- Surgery to cut away patches of endometriosis tissue if having fertility problems and hormone medications are not providing relief.
- As a last resort- an operation to remove part or all of the organs affected by endometriosis – such as surgery to remove the womb
- Some other things you can do at home may help with pain:
- Take warm baths.
- Put a hot water bottle or heating pad on your belly.
- Exercise regularly.
- Some women report relief from pain with therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or supplements, such as thiamine (vitamin B1), magnesium, or omega-3 fatty acids
Your doctor will discuss the options with you. Sometimes they may suggest not starting treatment immediately to see if your symptoms improve on their own.